Understanding Break-Even Points in Business

Intro
Understanding the concept of break-even points can be a game changer for anyone engaged in the world of finance. Whether you own a burgeoning startup or manage a well-established organization, grasping this fundamental principle is crucial. It offers insights into how costs, revenues, and profits mesh together, providing a clear picture of when your business starts turning a profit.
This guide lays out the complexities of break-even analysis, breaking down the calculations and the underlying concepts. By gaining a deeper understanding of this metric, you can make well-informed decisions, optimize investments, and project future earnings accurately. Let's dive into the nuts and bolts of what it means to determine break-even points, with special focus on the terms and strategies that can empower your financial acumen.
Understanding the Break Even Point
Understanding the break-even point is a cornerstone of savvy financial decision-making, especially in the realm of business. The break-even point—a critical juncture at which total revenue equals total costs—offers insight on whether a company is sailing smoothly or heading toward troubled waters. This analysis can be a game-changer for entrepreneurs, investors, and financial enthusiasts alike, as it lays the groundwork for various strategic initiatives.
One of the key elements of understanding the break-even point is its potential to aid in cost control. Without a grasp of fixed and variable costs, businesses may find themselves drowning in expenditures, leading to operational inefficiencies. Moreover, the break-even analysis helps in setting realistic revenue targets. When stakeholders know how much they need to sell to cover their costs, they can more effectively strategize their efforts.
Considering its role, the break-even point isn't just a tool; it’s a pivotal element in performance management. It provides clarity on what prices to set for products or services, ensuring that profit margins remain healthy while still appealing to the market.
To sum it up, understanding the break-even point is indispensable for any investor or business owner looking to maintain financial health and ultimately grow. It arms them with the information needed to navigate uncertain waters and make informed decisions.
Definition and Importance
To put it simply, the break-even point refers to the volume of sales or production at which total revenues equal total costs. In other words, the business isn't making a profit, but it's not losing money either. This distinction is crucial for determining a company's viability and planning future operations.
The significance of understanding this point cannot be overstated:
- Financial Planning: Knowing the break-even point allows businesses to effectively plan their fiscal strategies. It can dictate when to invest in marketing or expansion.
- Risk Assessment: This analysis aids firms in identifying risks associated with revenue fluctuations. A company with a higher break-even point may face greater risk if sales dip.
- Investment Decisions: Investors often scrutinize break-even points to assess the potential return on investment. A lower break-even point may suggest a less risky venture.
Historical Context of Break Even Analysis
The concept of break-even analysis isn’t new. It emerged as businesses began seeking better ways to manage costs and optimize profits during the early 20th century. As industries matured, the need to define boundaries where losses would stop and profits would begin became more apparent.
Historically, break-even analysis was largely a tool for large-scale companies producing goods. However, with the rise of service-oriented businesses and the gig economy, its applications expanded, leading smaller enterprises to adopt it as well.
One can also see the evolution of this analysis in connection with technological advancements. In the past, calculations were cumbersome and often inaccurate due to lack of proper data. Today, the digital landscape offers models and software that streamline these computations, making them accessible even to small businesses. This democratization of information means that anyone can gain insights into their financial positions, promoting smarter practices and informed decisions.
The growth of this analysis holds its roots in complex market dynamics, evolving alongside changes in business practices and consumer behaviors.
Core Elements of Break Even Analysis
The heart of break even analysis lies in understanding its core elements. Failing to grasp these components can lead to misguided decisions that could nip profitability in the bud. This section delves into the fundamental building blocks — fixed costs, variable costs, and various revenue streams — that not only lay the groundwork for accurate break-even calculations but also help in crafting effective business strategies.
Fixed Costs Explained
Fixed costs, as the name suggests, are expenses that do not change with the level of goods or services produced by a business. Whether you produce one unit or thousands, these costs remain constant within a certain range of production. Examples include rent, salaries, and insurance. Knowing your fixed costs is crucial because they form the baseline against which revenues are measured.
Understanding these costs helps make more informed decisions. If a business wants to expand its operation or invest in a new product, having a clear view of fixed costs allows for better forecasting and planning. For instance, a startup operating out of a small office knows that their rent will always be there, regardless of how many customers flow through their doors.
"You can know the ropes, but if you don't know your fixed costs, you're sailing blind."
Variable Costs Demystified
On the flip side, variable costs fluctuate in direct correlation with production levels. These include costs like raw materials, labor directly tied to production, and commissions. As the business scales up or down, so too does the amount spent on these costs.
Comprehending variable costs is vital for predicting profitability. If the variable costs per unit rise unexpectedly, the company might find itself in a tighter spot than anticipated. For instance, a bakery may see rises in flour prices, which influences the cost of each loaf produced, impacting pricing strategies and profit margins. Thus, keeping a close eye on variable cost trends can save a business from budgetary nightmares.
Revenue Streams
Lastly, understanding the various revenue streams a business has is imperative. This includes direct product sales, services rendered, and ancillary income sources like online consultations or content monetization. Each revenue stream contributes differently to overall cash flow and sustainability.
For instance, a fitness center might earn income from membership fees, personal training sessions, and merchandise sales. This diversity helps in risk mitigation because if membership numbers dip, revenue from personal training still keeps the lights on. Evaluating these streams provides insights into which areas are performing well and which could use a little TLC.
In summary, mastering these core elements of break even analysis empowers businesses to not just survive, but thrive. Each aspect — fixed costs, variable costs, and revenue sources — plays a distinctive role in shaping financial strategies, ensuring nimble responses to market changes.
Calculating the Break Even Point
Calculating the break even point is a foundational skill for anyone venturing into the realm of business operations. It's not just about numbers; it shapes decisions that can mean the difference between profit and loss. When a company understands its break even point, it gains insight into how many units need to be sold to cover costs. This knowledge is vital when setting prices, managing production levels, and planning for future growth. Knowing when your business turns from red to black can help in crafting strategies that align with your financial goals.
Break Even Formula Overview
The break even point itself can be encapsulated in a straightforward formula:
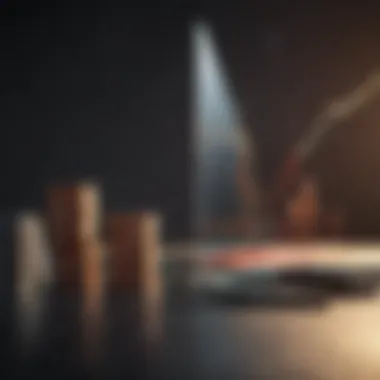

The formula highlights the key elements: fixed costs, variable costs, and the selling price. Each plays a crucial role in defining when profitability is achieved. The beauty of such a formula is its simplicity; however, the implications are more profound. By breaking it down into its components, businesses can pinpoint weaknesses in pricing strategy or cost management. Thus, having clarity on this formula allows a more calculated approach to financial forecasting.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Calculating the break even point involves meticulous attention to three core elements:
Identifying Fixed Costs
Identifying fixed costs requires a keen eye for static financial obligations. These are expenses that do not change with production levels, such as rent, salaries, and insurance. Understanding fixed costs is essential in the break even analysis, as they form the baseline from which all further calculations are made. The key characteristic of fixed costs is their consistency; they remain unchanged regardless of how much is produced or sold. This reliability makes them easy to project, but they can also be burdensome during lean periods.
A unique feature of fixed costs is their impact on the risk profile of a business. The higher these costs, the higher the sales volume required to cover them. This can be beneficial for established companies with stable demand, yet a double-edged sword for startups grappling with uncertain sales projections.
Determining Variable Costs per Unit
Variable costs are tied to production. They rise and fall as output levels change. Understanding these costs is vital because they help define the profit margin per unit. The main characteristic of variable costs is their dependence on the volume of goods produced; the more you make, the higher these costs climb. This variable nature makes them easier to adjust in response to market demand.
A unique feature of variable costs is the flexibility they offer. If production needs to ramp up or down, businesses can do so without impacting fixed costs. However, managing these variable costs is equally essential; if ignored, they can erode profitability, especially when unexpectedly high percentages cut into margins.
Assessing Selling Price per Unit
The selling price per unit is the golden ticket in the break even analysis. It's the revenue that businesses aim to achieve for each item sold. The most notable characteristic of the selling price is that it can often be adjusted through pricing strategies. Getting this right is crucial; too high, and you risk losing customers, too low, and you might not cover costs.
A unique aspect of assessing selling price per unit is its potential to influence both fixed and variable costs indirectly. By positioning a product smartly, a company might offset high fixed costs through increased sales volume or leverage purchasing power to reduce variable costs.
As you can see, calculating the break even point pulls together the threads of costs and pricing in powerful ways. Understanding that delicate balance is key to thriving in a competitive market.
"Master the art of numbers, and the world becomes a canvas for your ideas."
Advanced Break Even Concepts
Understanding advanced break even concepts arms decision-makers with a broader toolkit for financial strategy. These concepts play a critical role in detailed analysis and nuanced financial planning, enabling businesses to navigate complex environments and optimize their operations effectively. At the heart of these ideas lie two particularly important frameworks: Contribution Margin Analysis and Multi-Product Break Even Analysis. Both serve not just as academic exercises but as practical tools that can directly impact profitability and resource allocation.
Contribution Margin Analysis
Contribution margin analysis is a financial metric that helps businesses determine how much revenue remains after covering variable costs. In simple terms, it tells you how much of your sales will contribute to fixed costs and profit. The formula can be broken down as follows:
[ Contribution Margin = Selling Price - Variable Cost ]
This analysis provides critical insights into product pricing and cost structure, which can significantly influence business decisions. For instance, using this metric, a company can assess whether a product contributes enough to its profits or if it’s dragging the bottom line down.
Key Benefits of Contribution Margin Analysis:
- Informed Pricing Strategies: Helps in setting prices that cover costs while ensuring profitability.
- Profit Optimization: Identifies which products to focus on based on their contribution to overall profit.
- Cost Control: Highlights areas where variable costs can be reduced without sacrificing quality.
Furthermore, the contribution margin can be expressed as a ratio or percentage of sales. This provides an additional layer of perspective, indicating how effectively a company turns its sales into actual profit.
"Analyzing contribution margin offers a clear sight into which products are financially viable and which aren't, helping businesses streamline their offerings."
Multi-Product Break Even Analysis
As businesses often juggle multiple products at once, understanding the break even point across various product lines becomes essential. Multi-product break even analysis expands upon traditional break even analysis by taking into account variations in contribution margins among different products. The essence lies in distributing fixed costs among several products and calculating combined break even sales volume.
This approach involves several steps:
- Calculate the Contribution Margin for Each Product: As mentioned earlier, knowing the contribution margin for every product helps in reallocating resources wisely.
- Determine the Sales Mix: Establish how much of each product typically gets sold together.
- Calculate the Weighted Average Contribution Margin: By taking into account the sales mix, you can develop an average margin to use in break even calculations.
Through multi-product break even analysis, businesses can achieve:
- Enhanced Sales Forecasting: Understanding how changing product lines will affect overall profitability.
- Better Resource Allocation: Identifying which products to market aggressively and which may need reevaluation.
- Strategic Decision Making: Informing future product development based on financial outcomes.
Incorporating these advanced concepts into strategic discussions can significantly improve financial outcomes. Recognizing that not all products carry the same weight in achieving profitability is crucial in today’s competitive landscape. Business leaders need to go beyond mere sales figures and delve into how each product contributes to the overall health of the organization.
Thus, engaging with these advanced break even concepts enables a holistic understanding of business dynamics, giving companies the confidence to make informed decisions.
Practical Applications of Break Even Analysis
Understanding the practical applications of break even analysis is pivotal in leveraging the data it provides. It not only aids in strategic planning but also enhances overall financial competence. This method facilitates clarity in decision-making regarding pricing, investments, and operational efficiency within a business. Neglecting these applications can lead to missed opportunities or poor financial health. Here are some elemental ways break even analysis plays a vital role in business strategies:
- Pricing Strategies: Pricing is not simply about setting a number on a product; it requires a thorough understanding of costs and market conditions. Break even analysis provides extensive insights into how prices can impact profitability. By knowing the break even point, businesses can strategize their pricing to cover costs while ensuring competitiveness. For instance, a company selling gourmet coffee might decide to price their new blend just above the break even point after analyzing costs. This analysis helps them find a sweet spot where the price is attractive to customers but also profitable. Common strategies include:
- Investment Decisions: Investors often seek reliability in their investments. Break even analysis offers a clear framework for assessing potential investments. Knowing the break even point helps in determining the viability of a new venture. If a startup claims it can break even within a year, investors would be keen to delve deeper into the figures presented. This assessment aids not just startups but established companies in making informed expansion decisions, ensuring that potential risks are well understood and mitigated.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficiency isn't just about reducing costs; it's about optimizing all business processes, including production, labor, and distribution. Break even analysis can spotlight areas where a company might be overspending. By identifying fixed and variable costs, management can implement improvements. For example, let’s say a manufacturing firm discovers through break even analysis that its production cost is disproportionately high due to inefficiencies in the supply chain. The company can then strategize to renegotiate contracts with suppliers or streamline production processes accordingly. In a broader sense, achieving operational efficiency could entail:

- Cost-plus pricing, where businesses add a fixed percentage to their costs to ensure they cover expenses and realiz profit.
- Competitive pricing held against competitors, considering the break even point allows for effective adjustments to maintain market share.
- Analyzing operational workflows to improve productivity.
- Evaluating technology investments that can automate repetitive tasks and lower variable costs over time.
Break even analysis not only determines when a business will start making a profit but also serves as a compass for navigating through various strategic decisions.
Incorporating break even analysis into the core of business decision-making not only fortifies the foundation of sound financial practices but also cultivates an agility that is necessary in today's ever-changing marketplace. An effective grasp of this analysis promotes informed actions that might just catapult a business towards achieving its financial goals.
Limitations of Break Even Analysis
Understanding the limitations of break even analysis is crucial for a well-rounded financial perspective. While this tool serves as a reliable guide for financial decision-making and offers insights into profit potential, it is not devoid of drawbacks. Recognizing these limitations helps users avoid over-reliance on the model, thus refining their strategic planning efforts.
Static Nature of Analysis
One of the most prominent limitations of break even analysis is its inherently static nature. The basic premise relies on fixed costs, variable costs, and price remaining constant over time. However, in the ever-evolving business environment, factors such as market demands, competition, and operational expenses change rapidly. For instance, a manufacturer might set a break even point based on current production costs. Yet, if raw material prices skyrocket due to unforeseen circumstances, the initial calculations become irrelevant.
This rigidity can mislead decision-makers into assuming that the break even point remains constant, which is far from reality. It’s important to not treat break even calculations as set in stone. Rather, they should be revisited regularly to reflect more accurate conditions. So, to mitigate this risk, businesses can adopt a more dynamic approach, embracing flexible pricing strategies and regularly reviewing their cost structures.
Market Variability Considerations
Besides the static nature of analysis, market variability is also a significant consideration. The break even analysis often assumes a linear relationship between units sold and revenue generated. However, this overlooks the complexities of real-world markets, where customer demand can be swift and unpredictable. For example, an upward swing in consumer preferences towards sustainable products can render a previously calculated break even point ineffective.
Furthermore, external economic factors, such as inflation and recessions, create layers of uncertainty that break even analysis doesn’t account for. Strong competitors entering the market or shifts in consumer behavior can drastically alter cost structures and profit expectations.
"Understanding the limitations of your tools is as essential as knowing how to use them."
In essence, while break even analysis is a valuable tool, it should be complemented with other strategic planning methods. Utilizing sensitivity analysis or scenario planning can provide a more nuanced understanding of potential risks and opportunities in the market. Both static nature and market variability highlight the necessity for continuous adaptation when applying break even analysis in real-world situations.
Often, it’s not just about knowing where you stand today, but also about anticipating where you might find yourself tomorrow.
Visualizing Break Even Analysis
Visualizing break even analysis is crucial in understanding how a business can remain profitable. The ability to translate numbers into a visual format helps stakeholders grasp complex financial data quickly. A well-constructed visual representation makes it easier to identify the break even point at a glance, leading to informed decision-making in various situations. It’s like having a map in an otherwise uncharted territory; you can see where you need to go and what obstacles might lie ahead.
Key benefits of visualizing break even analysis include:
- Clarity: Graphs and charts simplify complex data, presenting clear insights into fixed costs, variable costs, and potential revenue.
- Identification of Trends: Patterns become visible over time, helping to understand seasonality or fluctuations in demand.
- Enhanced Communication: Visuals are often more effective than lengthy explanations when presenting to stakeholders or potential investors. They can see the bottom line without delving deep into numbers.
Understanding this visual representation can increase strategic alignment across departments. When marketing understands the pricing point needed to reach the break even point, they can more effectively target their campaigns.
"A picture is worth a thousand words; in financial planning, a graph can be worth a thousand dollars."
Graphical Representation of Break Even Points
When it comes to graphical representation, the break even point is often showcased through a graph that displays both total revenue and total costs against the number of units sold. Typically, two lines are drawn: one indicating total costs, which combine fixed and variable expenses, and another showing total revenue.
The intersection of these lines marks the break even point. At this point, a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. This illustration is fundamental because it allows any business operator to see how changes in pricing, cost, or sales volume will affect profitability.
In constructing a break even graph, one should consider key elements including:
- X-Axis: Usually denotes the number of units sold.
- Y-Axis: Represents revenue and costs in dollar amounts.
- Total Costs Line: This line rises gradually, starting from fixed costs and adding variable costs with increased sales.
- Revenue Line: This line should ideally have a positive slope reflecting sales growth.
While graphical tools like Excel or Google Sheets can be used to produce these visuals, more advanced software can offer customization and features that can enhance understanding. For those wishing to dive even deeper, software like Tableau can offer sophisticated visual presentations that can help track performance metrics over time.
Understanding the Break Even Chart
A break even chart is more than just a graph; it’s a visual story of a business's journey to profitability. Each element of the chart contributes to a fuller understanding of the underlying economics of a business. Breaking down what the different lines mean can enhance your grasp of how costs, revenues, and sales will impact overall financial health.
Components of a Break Even Chart:
- Break Even Point: The most critical aspect of the chart, where the total revenue line crosses the total cost line.
- Area of Profit: To the right of the break even point, showcasing potential profit increases as sales rise.
- Area of Loss: To the left of the break even point, illustrating losses incurred from poor sales performance.
Understanding these components allows business owners and stakeholders to make more informed decisions related to pricing adjustments, cost control measures, or sales strategies. It also highlights the importance of staying agile in the face of market changes, where a quick visual assessment can lead to timely and effective actions.
By incorporating visuals into this analysis, you're not merely crunching numbers; you're mapping out the future of your business.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Analyzing break-even points is not solely an academic exercise; it's a practical tool shaped by real-world experiences and a necessity for sound decision-making in business. Case studies add depth and relevance, providing compelling narratives that clarify the intricacies of break-even analysis in varied contexts. By exploring specific scenarios, we're better equipped to understand how businesses leverage this concept to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and ultimately enhance their financial strategies.


A robust body of case studies reveals how successful companies have effectively employed break-even analysis to identify optimal pricing strategies, manage costs, and meet their goals. It also highlights common pitfalls and offers lessons that some have learned the hard way. From startups to well-established corporations, the implications of a well-calibrated break-even analysis can be profound.
In essence, case studies demonstrate that theory comes alive in practice. They compel us to think beyond numbers and formulas, encouraging a holistic understanding that marries analytical rigor with creative problem-solving. By examining the particularities of various industries, we unearth valuable insights that speak directly to our financial objectives, creating an invaluable resource that promises much more than theoretical knowledge alone.
Industry-Specific Applications
When it comes to break-even analysis, no two industries are identical. Each field has its peculiarities, influencing how costs are structured and revenue is generated. Let's delve into several industry-specific applications where understanding break-even points becomes critical.
- Manufacturing Sector: In this space, fixed costs can be daunting due to large overhead expenses related to equipment and facilities. Companies such as Ford Motor Company utilize break-even analysis to determine the minimum number of units they need to produce to not just cover costs, but also to pursue profit goals. Adjusting costs, improving efficiency, or changing product lines can shift their break-even point significantly.
- Retail Industry: In retail, the relationship between fixed and variable costs can be heavily influenced by seasonal fluctuations. For example, holiday-specific retailers must consider how their sales will peak at certain times of year. Understanding their break-even point helps them strategize inventory, marketing spends, and sales pricing effectively.
- Service-Based Organizations: Companies such as consulting firms often face unique challenges identifying their break-even points, as fixed costs may relate more to personnel than products. A deep dive into cost allocation and productivity is essential. Knowing how many billable hours are needed to break even allows them to better manage talent and service delivery.
Such industry-specific insights demonstrate how tailored break-even analyses can predict the operational viability of a business. Without these customized approaches, decisions could be less strategic, leading to potential financial misalignment and decision-making errors.
Lessons from Small Business Startups
Small businesses often tread on thin ice, balancing dreams and realities. They frequently face unique circumstances that make understanding break-even points even more crucial. Here, we can draw lessons that not only pertain to financial prudence but also operational adaptability.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Startups like Zoom rooted their success in precise cost analyses. Knowing their break-even point early on guided them in setting manageable goals, focusing efforts on customer acquisition and retention without overspending.
- Testing the Waters: New businesses could opt for pilot programs that allow them to analyze break-even points on a smaller scale. For instance, a café might explore a limited-time menu, allowing them to gauge customer interest while assessing profitability without committing extensive resources.
- Emphasizing Customer Feedback: Startups that integrate customer feedback into their pricing models enhance their understanding of perceived value, thus producing a more accurate representation of their break-even analysis. This iterative process can lead to adjustments that enhance revenue quickly.
Sifting through the wealth of lessons from small business startups enables aspiring entrepreneurs to grasp how break-even analysis can be a lifeline for navigating initial challenges. Understanding not just the numbers but the operational framework surrounding them cultivates a sense of preparedness.
"Without a firm grasp on break-even analysis, small businesses risk sailing into unpredictable waters."
Integrating Break Even Analysis into Strategic Planning
Integrating break even analysis into strategic planning is not just a nice-to-have. It's a pivotal component that can significantly influence a business's trajectory. Understanding the dynamics of fixed and variable costs against revenue generation allows organizations to steer their strategies more accurately. Companies ought to revisit their break even points regularly since market conditions and operational costs don’t stay stagnant. This integration ensures that decision-makers are arming themselves with the most current data.
When businesses align their strategies with their break even analysis, they’re better equipped to formulate actionable plans that can mitigate risk while maximizing profitability. By factoring in these calculations into the strategic framework, organizations can also identify areas that need adjustments, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Aligning with Business Objectives
To achieve coherence in strategic planning, break even analysis must intertwine seamlessly with core business objectives. It’s prudent for decision-makers to ask: How does knowing the break even point help us meet our goals? Let’s break this down:
- Clarifying Financial Goals: Understanding the break even point provides a benchmark for profitability. It helps firms set realistic sales targets, which can serve as financial goals for the business.
- Risk Management: It highlights the vulnerability of a business to changes in costs or pricing. Being aware of where these vulnerabilities lie can lead executives to develop contingency plans to navigate uncertain waters.
- Resource Allocation: By knowing when they'll reach profitability, companies can allocate resources effectively. This means investing in growth opportunities when they're most likely to have an impact, rather than risking investments when they’re still in the red.
- Performance Evaluation: Organizations can utilize an established break even point to measure operational efficiency and sales performance. This allows for timely corrections if actual performance diverges from projections.
In tandem, these alignments drive not just financial performance, but also strategic coherence across business units, ensuring everyone is in sync with the overarching strategy.
Enhancing Financial Forecasting
An accurate break even analysis can significantly enhance a company's financial forecasts. Without it, forecasts can sometimes feel like tossing a dart in the dark. Breaking it down:
- Data-Driven Insights: Connnecting financial forecasts to break even analysis means you are challenged to think critically about your data. Are there historical patterns in costs or revenues that need to be factored in? Incorporating this kind of analysis transforms data into actionable insights.
- Scenario Planning: It enables firms to simulate various scenarios—what happens if costs rise, or prices drop? Scenario planning can highlight different paths a company might take, offering a clearer understanding of the potential risks and rewards of each.
- Investor Confidence: For businesses eyeing investment, a robust break even analysis indicates a level of financial acumen that usually resonates with investors. They’re much more likely to back those who demonstrate an understanding of their financial landscape.
"Integrating break even analysis into strategic planning isn't just about crunching numbers. It's a strategic necessity that can define business success."
Ultimately, enhancing financial forecasting through break even insights leads to more reliable and robust planning. Businesses that adopt these practices tend to experience a smoother ride, as they’re armed with the clarity and foresight needed in today’s dynamic environment.
Culmination and Future Considerations
In the realm of business, the ability to navigate financial waters effectively is paramount. The conclusion of our exploration into break-even analysis serves as a crucial juncture for any entrepreneur or investor. It’s not just about crunching numbers but understanding the broader implications of these calculations. The insights gleaned from this guide emphasize that break-even analysis is more than a mere tool; it’s a framework for strategic decision-making.
One of the key elements is the role of break-even points in future planning. Knowing where costs align with revenue provides a safety net. It informs pricing strategies, product line decisions, and helps identify when to ramp up production. Without this clarity, businesses might find themselves adrift in a sea of uncertainty, potentially leading to poor financial choices.
Additionally, it’s essential to keep in mind that market dynamics are constantly in flux. Thus, the ability to adapt your break-even calculations as inputs shift demonstrates a robust understanding of your business landscape. Remaining aware of both fixed and variable costs, as they evolve, empowers managers to pivot strategies efficiently.
In practical terms, ongoing review and adjustment of break-even analyses can unlock opportunities for improvement in operational efficiencies and profitability. With the right approach, companies can transform these insights into action points that enhance financial health and sustainability.
"What gets measured gets managed."
This statement rings particularly true in the realm of break-even analysis. By incorporating these insights into daily business operations, one can establish a culture of financial acuity and proactive strategy.
Considering the future, embracing technology for better data analysis and visualization will allow businesses to refine their break-even models continually. The integration of software tools and analytical platforms is no longer a luxury but a necessity to keep pace with competition.
In summary, both the understanding and application of break-even analysis should be viewed as living components of a business framework. Keeping it dynamic, responsive, and aligned with organizational goals will lead to better foresight and strategic positioning.
Summary of Key Insights
Reflecting on the insights derived from our guide, several key points stand out:
- Understanding Costs: Recognizing the distinctions between fixed and variable costs is fundamental to accurate break-even calculations.
- Importance of Revenue Streams: Clear insight into how revenue is generated is crucial for determining break-even points effectively.
- Real World Applications: Businesses that master break-even analysis can employ it to inform decisions related to pricing, investment strategies, and overall operational efficiency.
- Continuous Adaptation: Given that market conditions can shift, regularly revisiting and recalibrating break-even calculations is essential for sustained success.
The Evolution of Break Even Analysis
The concept of break-even analysis has undergone significant transformation since its inception. Historically, it emerged as a straightforward method for businesses to assess when they would start making profits. But as the landscape of business and economics shifted—thanks to technological advancements and data analytics—the approach to break-even analysis evolved.
In the past, operations focused heavily on static calculations. However, in our fast-paced environment, businesses leverage dynamic models that account for fluctuations in costs, pricing strategies, and multi-product scenarios. This evolution reflects broader trends in economics, particularly the rise of iterative and agile business practices.
Moreover, with the advent of forecasting tools and software, companies can now simulate various scenarios to predict break-even points under different conditions. This predictive analysis is pivotal. It allows for more informed decision-making, where businesses can run “what-if” scenarios that reveal the impact of market changes.
Equally important is the shift towards integrating break-even analysis into strategic decision-making processes. Today, it's not just a standalone calculation; it aligns with broader financial forecasting and strategic objectives. As businesses face increased competition and economic fluctuations, having a robust understanding of break-even dynamics is invaluable.



